Diabetic Foot
Diabetes is a combination of several diseases with elevated blood glucose levels affecting various organs like eyes, kidneys, heart, blood vessels. It reduces the body’s ability to fight infection. Over time it impairs the immune system of the body. Foot problems occur commonly in diabetics and soon become serious.
When the nervous system is damaged the feet become numb. The normal sweat and lubrication of the skin is impaired. These factors lead to abnormal pressures on the skin, bones and joints during walking leading to breakdown of the skin of the foot. Sores develop. The damage to the blood vessels and the immune system prevents wound from healing. Bacterial infection of the bones, skin, muscle and connective tissue may occur which may develop into gangrene. Because of the poor blood-flow antibiotics cannot get to the site of infection easily. Then the only way our is amputation of the leg or foot. Should infection spread to the blood stream it may become life threatening.
Diabetics must be fully aware of how to prevent foot problems, to recognise them early and seek the right treatment. Though the treatment has tremendously improved still prevention and control of blood sugars remains the best way to prevent complications.
Diabetics must be educated so that people can :
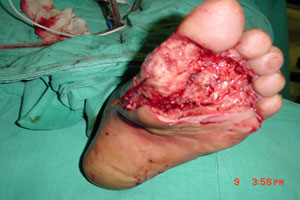
After Debridement ( clean up )
- Examine their feet and recognise the early signs and symptoms of diabetic foot problems.
- How to manage routinely home foot care, to recognise when to call a doctor, and when the problem becomes serious enough to go to the casualty.
Causes of diabetic foot:
- Footwear – poorly fitting shoes commonly lead to diabetic foot problems. If red spots, blisters, corns, hardened foot skin and constant pain on wearing shoes occur new properly fitting shoes must be brought right away. If diabetic has flat feet, bunion, or hammer toes shoe inserts may be necessary.
- Nerve damage – this happens in long standing diabetes (peripheral neuropathy). These people are unable to feel their feet properly and sense the position of the feet while walking and balancing. They cannot feel the shoes rubbing which normal people can. They are unable to sense minor injuries to the feet, tears and foot strain. For instance if there is a small stone in the shoe we all take it out before it hurts us. In diabetics they do not feel it and so it damages their feet and creates sores.
- Poor circulation – poorly controlled diabetics have hardening of the arteries or atherosclerosis. This leads to poor blood flow and delayed healing.
- Foot trauma – increases risk of serious infection.
- Infections – fungal infection of the toenails can lead to bacterial infection and serious complications. So it must be treated promptly.
- Ingrowing toenails must be dealt with immediately by a specialist.
- Smoking – chokes the arteries, reducing the blood supply thus increasing the chances of infection and amputations. Stop smoking is a must.
Diabetic foot symptoms
- Persistant pain – sprain, strain, bruise, underlying infection or poorly fitting shoes.
- Redness shows infection.
- Swelling – in inflammation or infection due to poor fitting shoes.
- Poor circulation – presents as pain on walking and improves with rest (caludication). Absence of hair growth on the lower leg and feet. Hard shiny skin on legs.
- Localised warmth may be sign of infection.
- Break in skin is serious due to abnormal wear and tear, injury and infection.
- Calluses and corns show chronic trauma to foot.
- Toe fungus and ingrown toenails may lead to serious bacterial infection.
- Pus drainage shows infection.
- Limp may be because of serious infection or poorly fitting shoes.
- Fever with chills with wound in foot is sign threat to limb or life.
- Red streak away from wound is spreading infection.
- New numbness is sign of nerve damage and chances of foot damage.
When to seek medical care?
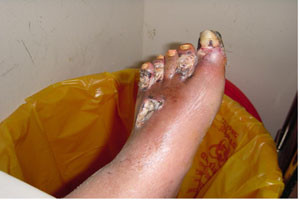
Gangrene of toes in diabetic
Any significant trauma to the leg needs medical attention. Even minor trauma may lead to serious infection. Pain in the leg or foot demands consultation. Contact your doctor in case of wounds. Warmth, swelling and redness are signs of infection and need to be addressed. New constant numbness is due to neuropathy and reduced blood supply calls for care. Walking difficulty may be due to sores on the feet or infection and should be tackled. Constant itching is a sign of fungal infection. Corns should be removed professionally. Fever should be looked into by a doctor. Severe pain is due to loss of circulation in the leg, serious infection or nerve damage. Ulcers on the foot are in danger of limb threatening infection. Recent confusion is not a good sign as it may depict sepsis from diabetic foot and may be limb or life threatening.
Examination
- Examination of the vital signs, sensation in the legs and the feet and the pulses in the legs.
- Laboratory tests –
- Blood tests – complete blood count in case of severe infection. High or low white cell count shows severe infection.
- Blood sugar should be tested.
- Renal function and electrolytes are a must.
- Liver and cardiac enzymes are done to see if there is any damage due to infection.
- X-Rays – of the bones of the legs and the feet to see if there is infection. Gas in the soft tissue – life threatening gangrene.
- Colour Doppler study – flow in the arteries and veins.
- Angiogram – this is done if surgery is needed to improve circulation.
Diabetic Foot Treatment
- Selfcare at home
- Foot examination – daily examine feet and use water based moisturizer to keep skin soft and prevent dryness. Wear cotton or wool socks. No elastic stockings as they may compress the arteries.
- Eliminate obstacles that are oddly placed in your home to avoid any injuries. Light night pathways used indoors and outdoors.
- Toenail trimming – always use clippers, never scissors or blades. Cut them straight across to avoid ingrowing toe nails. If eyes are a problem then get a specialist to do them for you.
- Footwear – wear comfortable footwear.
- Exercise – improves bone and joint health in legs and feet, improves the circulation in the legs and stabilizes blood sugar levels.
- Smoking – Quit smoking any form of tobacco. It accelerates damage to the small blood vessels leading to poor circulation which is a major risk factor for infections and amputations.
- Diabetic control – by taking diabetic diet, medications, regular checking blood sugar and exercising regularly. This reduces damage to the eyes, kidneys, blood vessels, nerves and the heart.
- Medical treatment
- Antibiotics – should be prescribed if wound is infected or is in high risk of infection. Full course must be taken. If it is limb threatening or life threatening hospital admission is done and I/V antibiotics are given.
- Follow-up
- Regular visits to the doctor and let the doctor know if condition is not improving.
- Be sure to finish the entire course of antibiotics otherwise resistance develops.
- Reduction of pain, swelling, improving ulcers and no fever is a good sign. Improvement should occur in the first 2-3 days. If there is wound infection good sugar control is needed for ulcer healing and preventing further ulcers.
- Prevention
- Good diabetic control.
- Regular foot self examinations.
- Knowledge on how to recognise the problem.
- Choosing proper footwear.
- Regular exercise.
- Avoid injury.
- Yearly monofilament tests to test sensation.
- Outlook
- Age – the older the patient the more the chances of leg and feet problems. There may also be circulatory problems. Elderly are also more prone to having trauma to the feet.
- Duration of diabetes – the longer the duration the more chances of lower extremity involvement.
- Seriousness of infection – if it leads to gangrene it would need amputation and there is a high risk of death. Ulcers over 1 inch across have a higher chance of amputation even with proper treatment. If infection involves deep tissue and bones the risk of amputation is very high.
- Quality of circulation – it is likely to be bad if patient is a smoker with diabetes and this naturally prevents healing. The chances of amputation rise sharply.
- Compliance with treatment plan – this is very vital to the proper improvement.